According to the National Scoliosis Foundation, approximately six to nine million people in the United States are affected by scoliosis. Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine. Scoliosis primarily affects children and adolescents. When a child is diagnosed with scoliosis, it can be very overwhelming for the parents to work towards the best treatment plan for their child. We have created an easy guide to scoliosis for families to gain a better understanding of their child’s condition and treatment options.
Types of Scoliosis
- Idiopathic: Idiopathic scoliosis simply means that the cause is unknown. The majority of cases of scoliosis are idiopathic and cannot be attributed to any specific reason or cause.
- Neuromuscular: Neuromuscular scoliosis is abnormal curvature of the spine as the result of a neurological and muscular diseases such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and spina bifida. Neuromuscular scoliosis often is a more progressive type and has a higher incidence of surgical intervention.
- Congenital: Congenital scoliosis is a form of scoliosis that arises from abnormal developmental while in the mother’s womb. Essentially, a child is born with scoliosis.
Diagnosis of Scoliosis
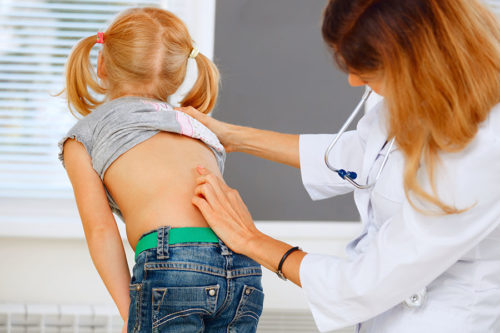
Scoliosis screening is an integral part of well child check-ups, especially as your child approaches puberty and adolescence. Scoliosis is usually first identified through a physical exam performed by your child’s pediatrician. The provider will have the child stand up and lean forward while looking for abnormalities in the curvature of the spine. If your child’s provider identifies a concern, imaging such as x-rays and MRI will be used to confirm the diagnosis and extent of the scoliosis.
The Cobb Angle is the angle used to measure the degree of curvature in the spine. The severity of scoliosis can be determined by the degrees of curvature the physician measures using the Cobb Angle. Curves can be either a single C shaped curve or two S shaped curves. Mild cases of scoliosis are usually those less than 20 degrees. Moderate scoliosis typically is categorized by curves that are between 25 and 50 degrees and severe scoliosis is classified by curves larger than 50 degrees.
Treatment of Scoliosis
There are many factors that are included in the treatment plan of a child with scoliosis. The age of the child and whether or not they have hit puberty and stopped growing are major considerations when determining what the most effective scoliosis treatment plan is. Additionally, gender plays a role as girls have been found to be more likely to have progression of scoliosis as they grow when compared to boys. The degree of scoliosis is also taken in to account.





